The most common solar panel types currently available are monocrystalline solar panels, polycrystalline solar panels (also called multicrystalline solar panels), and thin-film solar panels. A solar panel may differ in how it is made, in appearance, in performance, in cost, and in the type of installation for which it is most appropriate. There may be a better option for your application than another, depending on the type of installation you have in mind.
The major types of solar panels
Polycrystalline, monocrystalline, and thin-film solar panels are the three main types. The type of solar panel that is best suited to your installation depends on a wide range of factors, including the property you own and the characteristics of your desired system. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Major types of solar panels
Here we will discuss some common questions and concerns about solar panels and how they differ. What type of solar panel is best?
- The most efficient solar panels are crystalline panels.
- All crystalline panels are more efficient than monocrystalline panels, which are 15-20% efficient.
- The most cost-effective option is polycrystalline panels, which are between 15 and 17% efficient.
- The most resilient solar panels are thin film solar panels, which are best suited to unorthodox roof styles.
What are different solar panels made of?
Solar cells convert light into electricity using a semiconducting material. Silicon is the most commonly used semiconductor in solar cell manufacturing.

Monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels
Solar panels made of monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon wafers both use silicon wafers as cells. The wafers are arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle, covered with a glass sheet, and framed together to build a monocrystalline or polycrystalline panel.
Both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels use silicon cells, but their silicon compositions differ. A monocrystalline solar cell is made from a single, pure crystal of silicon. As an alternative, polycrystalline solar cells are made by melting silicon crystal fragments together in a mold before being cut into wafers.

Thin-film solar panels
There are a variety of materials used in thin-film solar panels, unlike monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is the most commonly used thin-film solar panel material. Thin-film panels make use of CdTe, a layer of transparent conductivity, to capture sunlight. In addition to the thin-film technology, a glass layer is applied on top for protection.
As with monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, thin-film solar panels can also be made from amorphous silicon (a-Si). In spite of the fact that these thin-film panels contain silicon, they are not made of solid silicon wafers. Rather, they are made from non-crystalline silicon that has been placed on top of glass, metal, or plastic.
A thin-film technology called Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) is another popular type of thin-film. Electrodes are placed on the front and back of CIGS panels to capture electrical currents, and the four elements are arranged between two conductive layers (glass, plastic, aluminum, or steel).
What do different solar panel types look like?
There are differences in the appearance of solar panels based on material differences and production methods:
Solar panels with monocrystalline crystals are the most efficient
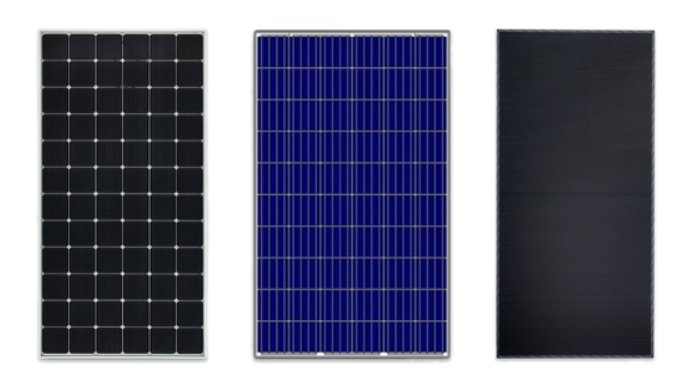
Most likely, you’re looking at a monocrystalline solar panel if you see black cells. The pure silicon crystals in these cells make them appear black because light interacts with them.
There are different colors for the back sheets and frames of monocrystalline solar panels, despite the fact that the solar cells themselves are black. Black, silver, or white is the most common color for the solar panel back sheet, while black, silver or white is the most common color for the metal frames.
Solar panels made of polycrystalline crystals are generally more cost-effective
A polycrystalline solar cell has a bluish tint because it reflects light differently than a pure monocrystalline silicon wafer because the light is reflected off silicon fragments within the cell.
In polycrystalline panels, the back sheets and frames are different colors, similar to monocrystalline panels. There are usually silver frames on polycrystalline panels, as well as white or silver back sheets.
Thin-film solar panels
A thin-film solar panel’s main aesthetic advantage is its low-profile and thin design. In contrast to other panel types, thin-film panels are often slimmer. As a result, the solar panels are roughly 350 times thinner than monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels.
A thin-film panel may be thicker than a monocrystalline or polycrystalline panel if it includes a thick frame. Thin-film cells themselves may be thinner than traditional solar cells, but entire thin-film panels may be similar in thickness to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. As close to the roof as possible, adhesive thin-film solar panels are available, but there are also more durable thin-film panels with frames as thick as 50 millimeters.
Based on the material used, thin-film solar panels come in either blue or black colors.
Solar panel power and efficiency ratings
The amount of power produced by each type of solar panel varies.
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels
The monocrystalline panel has the highest efficiencies and power capacities of all panel types. In contrast, polycrystalline panels usually have efficiencies between 15 and 17 percent, while monocrystalline solar panels have efficiencies as high as 20 percent.
Solar panels with monocrystalline crystals tend to produce more power due to both their efficiency and the fact that they are available in higher-wattage modules. Most monocrystalline solar panels are capable of producing more than 300 watts (W), while some are even capable of producing even more than 400 watts. Conversely, polycrystalline panels have a lower wattage.
There is no physical difference between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels – in fact, both types of panels tend to have 60 silicon cells each, usually with 96 or 72 cells (for large-scale installations). In spite of this, monocrystalline panels can produce more electricity even with the same number of cells.
Thin-film solar panels
In comparison to monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels, thin-film panels tend to have lower efficiency and power capacities. Materials used in the cells can affect their efficiency, but they typically have efficiencies closer to 11 percent.
It is not possible to produce thin-film solar panels with uniform sizes, as opposed to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels that are available in 60, 72, and 96 cell variants. As a result, thin-film panels have different power capacities based on their physical size. Generally speaking, monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels will have a higher power density per square foot than thin-film panels.
There are varying costs associated with different types of solar panels
There are differences between monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin film manufacturing processes; therefore, each type of panel is priced differently.
Most expensive option: monocrystalline solar panels
Among all types of solar panels, monocrystalline panels are likely to be the most expensive. Due to the manufacturing process, manufacturers have to absorb the costs associated with creating silicon crystals, which are used in solar cells. Known as the Czochralski process, this method is energy-intensive and results in waste silicon (which can later be used to manufacture polycrystalline solar cells).
Middle ground decision: Polycrystalline solar panels
The cost of polycrystalline solar panels is typically lower than that of monocrystalline solar panels. The cells are made up of silicon fragments instead of pure crystals of silicon. As a result, cell manufacturers and consumers will benefit from a much simpler manufacturing process.
It depends: Thin-film solar panels
A thin-film solar panel’s price depends largely on its type; CdTe panels are generally the cheapest to manufacture, while CIGS panels are more expensive than amorphous silicon panels and CdTe panels.
Due to additional labor requirements, thin-film solar panel installations are likely to be cheaper than monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panel installations. Due to their lighter weight and maneuverability, thin-film solar panels require less labor, making them easier for installers to carry up onto rooftops and secure. Consequently, labor costs can be reduced, resulting in a less expensive solar installation.
What type of solar panel is best for your installation?
When selecting the type of solar panel for your system, you’ll need to consider your property’s specifics and your surroundings. Each of the three types of panels, monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the solution that works best for you depends on your property and your goals.
A polycrystalline solar panel can be installed at a lower price and with lower efficiency for property owners with a lot of space for solar panels. In order to maximize your electric bill savings, monocrystalline solar panels are a great solution if you have limited space.
Solar panels made from the thin film are typically installed on large, commercial roofs that can’t support the additional weight of traditional solar equipment. Due to their larger surface area, thin-film panels can also be used on these types of roofs despite their lower efficiency. In addition, thin-film panels can sometimes be useful for portable solar systems, such as those on RVs or boats.
Thanks for reading.
